![]() Print this Article
Print this Article ![]() Share with friends
Share with friends ![]() Bookmark to Favorites!
Bookmark to Favorites!
Gout Cause: What Cause Gout? (Disease)
"Gout is often associated with men over 50 years, with overweight, including a diet too rich and often excessive alcohol consumption.
Nevertheless the youth and women are also targets of the gout. Discover what cause gout and the main risk factors for gout."
Article by: Gout
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Rate this article (4864 votes)
Rate this article (4864 votes)
Which are the causes of gout?
When the level of uric acid increases, due to the inability of kidney to pass it off to bladder, it starts to be accumulated in the blood in different parts of body like joints, knees, etc. This excess amount of uric acid forms tiny thin crystals in different parts of body especially in the joints, ankles, and more.
• Obesity, excessive weight gain (especially in youth),
• Moderate to heavy alcohol intake
• High blood pressure
• Unhealthy eating habit, especially junk food
• High protein-rich food
• Fructose in corn syrup found in soft drinks
• Abnormal kidney function.
• Nose or throat disease
• Heredity or genetic causes
• People who do not wear comfortable shoes and in improper way suffer from gouts. In
patients at risk of developing gout, certain conditions can precipitate acute attacks of gout.
These conditions include:
• Dehydration
• Injury to the joint
• Fever
• Recent surgery
• Certain drugs, such as thiazide diuretics (hydrochlorothiazide [Dyazide]), low-dose aspirin,
niacin, cyclosporine, tuberculosis medications (pyrazinamide and ethambutol), and others can also cause elevated uric acid levels in the blood and lead to gout.
•Certain diseases lead to excessive production of uric acid in the body. Examples of these
diseases include leukemia, lymphomas, and hemoglobin disorders.
Gout Cause: Are you a person with a risk to have gout?
Here are the main targets of the gout. If you are in these risk groups, take your precaution right now!
- Men between the ages of 30 and 50 years old (90% of cases),
- Pregnant women and women over 60 years after menopause (10% of cases),
- Genetic or family predisposition (18% of cases),
- People with high levels of uric acid,
- Obese people,
- People with excessive consumption of alcohol (mainly among drinkers of beers, due to the high concentration of purines),
- People who like eating offal, anchovies, consommés, seafood, asparagus, spinach, legumes, tripe (red kidney).
- People who regularly take a medicinal drug even at low doses (including diuretics or aspirin),
- People who suffer from psoriasis or renal failure,
- People who follow a treatment of chemotherapy or diuretics,
- People who lose weight fast or follow fasting.
Browse by Categories
About the Gout
Gout symptoms
Discover the main symptoms of gout on the body: fever, joint swelling, pain, and more.

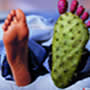
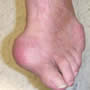
Gout toe photos
Discover surprising photos of the gout toe of the foot and other deformations: ear, hand, feet...

Gout treatment
Discover a selection of the best treatments for gout: paracetamol, colchicine, etc...
Glossary about Gout
Uric acid
Substance that is the cause of gout (if rate greater than 0,08 g/l), which is derived from the degradation of purines...
[+] Learn more about uric acid

Purines
Substance located in food (beer, anchovies, etc) which in excess cause gout. They help our DNA...

Tophus or Uric acid crystals
Clusters of uric acid crystals that cause deformation on the joints and the under the skin... 

Full glossary about Gout [+] more
Allopurinol: A medical drug that is used to lower the levels of uric acid in the blood.
Drugs for gout: a medical drug that decreases the inflammation caused by gout.
Gouty arthropathy: Destruction of the joints due to tophus (cluster of uric acid crystals).
Kidney stones: « stones » mainly created in the urinary tract.
Colchicine: medical drug that relieves gout pain (also used in prevention) learn more about colchicine
Renal colic: very intense lower back pain due to "stones" that close up the urinary tract.
Hyperuricemia: uric acid rate in the blood above the normal rate (> 420 µmol/l or 70 mg/l).
Hypouricemia: medical treatment to reduce the level of uric acid in the body.
Infiltration: injection of a product directly into a joint.
Renal failure: progressive, important and definitive degeneration of the kidney function.
Psoriasis: chronic disease that affects first the skin.
 Popular:
Popular: