![]() Print this Article
Print this Article ![]() Share with friends
Share with friends ![]() Bookmark to Favorites!
Bookmark to Favorites!
Gout Diet: Foods To Avoid With Gout (diet gout)
"Gout is often associated to obesity, overweight, general metabolism disorders, and thus an increase in the risk of cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis. It has been shown that excessive consumption of beer causes gout.
We can tell you the truth: cure the gout is possible, but only with some important diet changes"
Article by: Gout
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Rate this article (4864 votes)
Rate this article (4864 votes)
Gout diet: What is the gout diet?
A diet low in purine is recommended and a significant reduction in alcohol intake. Especially, the beer must absolutely be stopped because it contains purines which are transformed into uric acid (included non-alcoholic beer).
Tea is also to avoid because it contains a significant amount of purines (half as beer) and promotes the removal of water by the body, which can cause a sudden gout pain.
A gout diet is recommended with low purine foods:
- Avoid alcohol (especially beer), tea, offal, anchovies, seafood, asparagus, spinach, peas, lentils, consommés, sauces, cheese, fried foods, cocoa.
- Drink a lot of plain water without dry residues (see packaging label).
- Foods to reduce gout: cherries, strawberries, dairy products 0%, integral bread, tuna, salmon, celery. Vitamin C decreases gout (500 mg/day for 2 months).
- Diuretic medical drugs often prescribed for high blood pressure, can cause gout disease (they reduce the ability of the kidney to eliminate uric acid)
Foods To Avoid With Gout (gout diet)
Generally, it's important to reduce caloric consumption, and follow a diet low in purines, which excludes the following foods:
Foods to reduce | Foods to avoid | |
Beverage |
Champagne Soft drinks (light soft drinks allowed) Fruit juice rich in fructose (Apple juice, orange juice, grape juice) |
Spirits (brandy, whisky) |
Meat |
Poultry, rabbit Ham |
Sausages and Deli meats Venison and goose Meat broth, consommés |
Fish |
Eel, trout |
Mussels Scallops Other seafood Fish eggs |
Vegetables |
Vegetable soups | |
Cereals |
Whole grain breads | |
Dairy products |
|
Tips to avoid gout disease and gout pain
Spa treatments are prescribed as preventive treatment to relieve the gout pain.
Physical inactivity and overweight are aggravating factors of gout. Thus, it's advisable to practice exercise (swimming for example), stretching and moving joints: take care to repetitive movements and weight.
Finally, sudden changes in food, or weight gain, or weight loss can also cause gout. Foods that reduce the risk of gout are dairy products 0%, C vitamin (at least 500 mg/d), cherry and coffee.
Coffee: main food to prevent gout
A team of researchers from Harvard, school of public health (Boston), highlighted in early 2007 that people drinking a lot of coffee have less risk to have a gout disease.
The risk of gout disease would be less than 40% of those persons drinking 4-5 cups of coffee a day and 61% beyond. The effect is even more marked among men who don't take diuretics, another factor of risk of developing this disease. In the latter, the consumption of 6 cups of coffee or more is associated with a decrease of 70% of the risk of gout.
Another study showed that the coffee would reduce uric acid. Indeed, those drinking 4-5 cups of coffee per day have a lower average rate of uric acid than those who doesn't drink any (0.26 mg/dl).
Browse by Categories
About the Gout
Gout symptoms
Discover the main symptoms of gout on the body: fever, joint swelling, pain, and more.

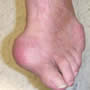
Gout toe photos
Discover surprising photos of the gout toe of the foot and other deformations: ear, hand, feet...

Gout treatment
Discover a selection of the best treatments for gout: paracetamol, colchicine, etc...
Glossary about Gout
Uric acid
Substance that is the cause of gout (if rate greater than 0,08 g/l), which is derived from the degradation of purines...
[+] Learn more about uric acid

Purines
Substance located in food (beer, anchovies, etc) which in excess cause gout. They help our DNA...

Tophus or Uric acid crystals
Clusters of uric acid crystals that cause deformation on the joints and the under the skin... 

Full glossary about Gout [+] more
Allopurinol: A medical drug that is used to lower the levels of uric acid in the blood.
Drugs for gout: a medical drug that decreases the inflammation caused by gout.
Gouty arthropathy: Destruction of the joints due to tophus (cluster of uric acid crystals).
Kidney stones: « stones » mainly created in the urinary tract.
Colchicine: medical drug that relieves gout pain (also used in prevention) learn more about colchicine
Renal colic: very intense lower back pain due to "stones" that close up the urinary tract.
Hyperuricemia: uric acid rate in the blood above the normal rate (> 420 µmol/l or 70 mg/l).
Hypouricemia: medical treatment to reduce the level of uric acid in the body.
Infiltration: injection of a product directly into a joint.
Renal failure: progressive, important and definitive degeneration of the kidney function.
Psoriasis: chronic disease that affects first the skin.
 Popular:
Popular: